-
Firsts in
POWERGRID -
Transmission
Asset Management -
POWERGRID Transmission System in Numbers
Firsts in POWERGRID
POWERGRID has been a leader in Indian Power Transmission Sector in terms of adoption of latest State of the art for improved operational efficiency of transmission assets. Since its inception, it has focused on integration of upgraded technologies in Power Transmission. Major operational highlights during its journey has been
-
1980
220kV D/c Bairasul – Pong put in service on 18th May, 1980 - Oldest asset in POWERGRID’s network
-
1984
400kV Hyderbad Station commissioned on 20th Sept, 1984- Oldest substation in POWERGRID
-
1989
First Back-to-Back HVDC terminal established at Vindhayachal substation
-
1990
First 500kV HVDC bipole link established (Rihand-Dadri)
-
1991
First SVC commissioned at Kanpur, Uttar Pradesh (±140 MVAR)
-
1997
First GIS commissioned at 220kV Kayankulam substation - Station handed over to NTPC in 2007
-
2007
First 765kV AIS commissioned at Seoni, Madhya Pradesh
First 400kV GIS commissioned at Maharanibagh, Delhi
-
2012
Trial development of world’s first 1200kV test substation at Bina, Madhya Pradesh
-
2013
Commissioning of 765kV Raichur-Solapur Transmission Line - Creation of One nation one grid one frequency
-
2014
Estbalishment of National Transmission Asset Management Centre (NTAMC) at Manesar, Gurugram (Haryana)
-
2015
Commissioned world's longest (about 1800 KM) multi-terminal ±800kV HVDC link between Agra and Biswanath Chariali
-
2019
World's highest altitude (above 11500 ft. or 3500 m) GIS station commissioned at Drass, (UT of Ladakh)
-
2020
Developed India's first 400kV digital substation by retrofitting conventional control and protection system at Malerkotla, Punjab
-
2021
India's first VSC based HVDC link commissioned between Pugalur and Thrissur
-
2021
World's first 400kV Natural Ester oil based shunt reactor
Transmission Asset Management
Power Grid Corporation of India Limited, a transmission licensee, takes continuous action regarding operation and maintenance of its transmission assets to ensure compliance with prescribed standards as well as to achieve high availability of the system for uninterrupted power supply to customers. POWERGRID’s O&M activities are ISO certified and systems and procedures are revised periodically to abreast with the technology.
POWERGRID’s transmission asset life-cycle management, risk management, and asset-related supporting activities are intended to support decisions on the optimal maintenance and renewal strategies, allocation of scarce resources and employment of reactive or proactive approaches.
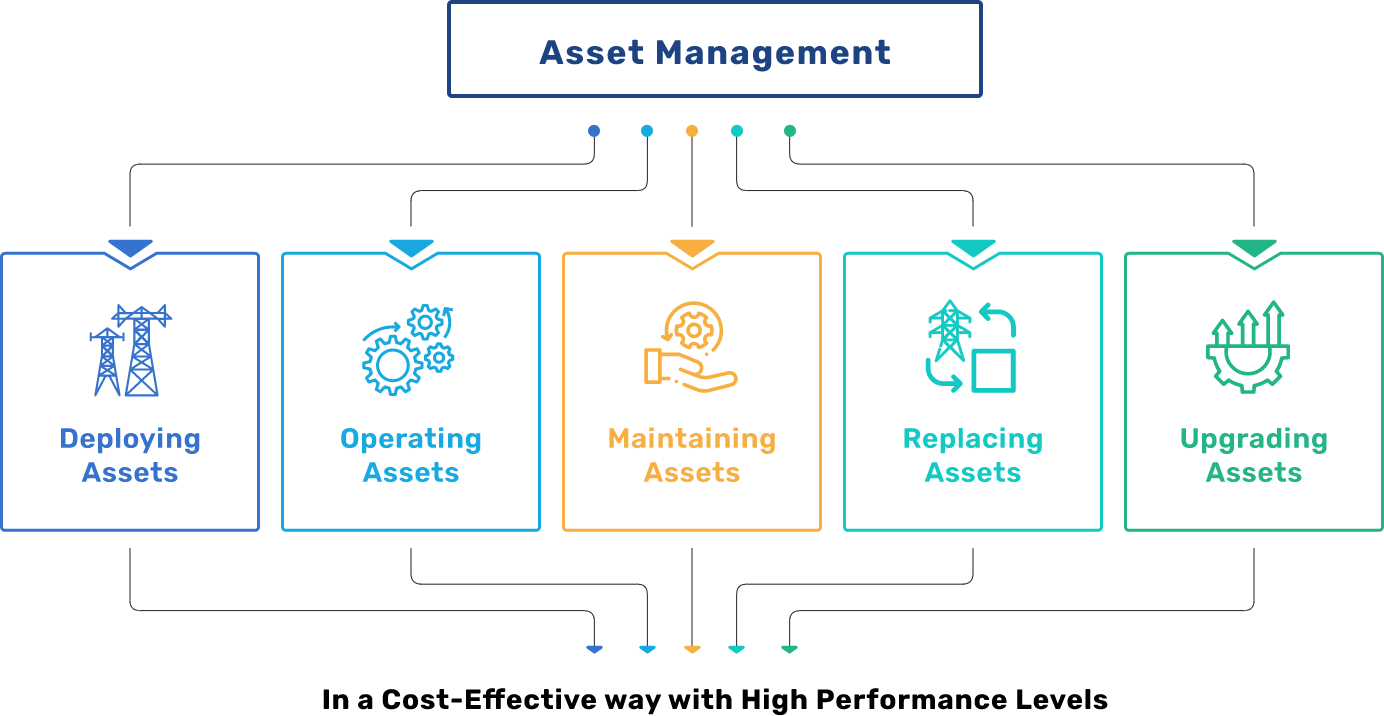
Asset managers are responsible for keeping assets healthy and operational, maintaining and optimizing asset life-cycle cost and value in a long-term perspective based on asset criticality and failure predictions. Designing replacement and maintenance programs implies achieving optimal capacity, higher equipment effectiveness, reliability and flexibility of the system, and as a result, lower maintenance costs, higher profit-making capability and increased financial returns on assets.
Transmission Line Maintenance Practice
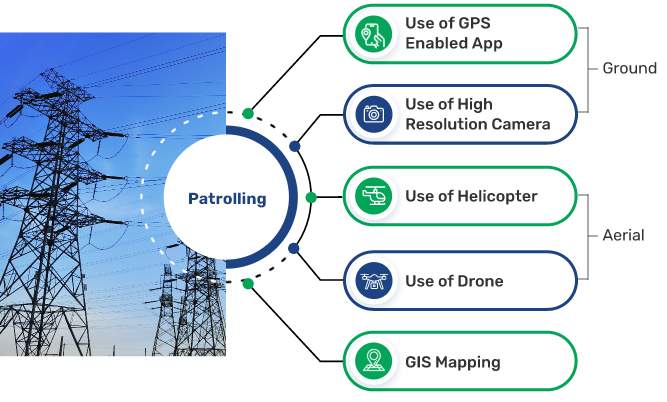
Substation Maintenance Practice

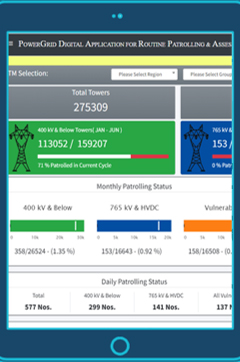
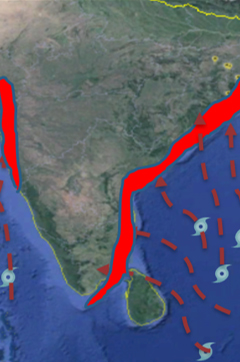
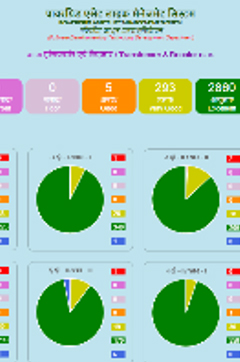
In terms of Operation and Maintenance of assets, POWERGRID has adopted several innovations in the last 5 years to improve system efficiency. Some of these are
CAPACITY Carrying 45% of India’s Transmission Capacity
-
18
HVDC
substations -
63
765kV
Substations -
168
400kV
Substations -
20
SVC/
STATCOM -
64
GIS
Substations -
>290000
Transmission
Towers -
>3800
Transformers
and Reactors
System Availability (%)
Tripping/ Line